SLAM and Navigation
-
We introduce the pose-graph topological integrity, an approach designed to assess the correctness of pose graphs
in simultaneous localization and mapping.
Traditional map quality assessment methods cannot capture the inconsistencies
between the constructed map and the actual environment.
The proposed approach utilizes heat kernel signatures to directly quantify topological inconsistencies
between the pose graph and support graph derived from free-space constraints.
This enables a multi-scale and per-vertex evaluation of topological integrity.
-
 S. Xie, K. Sakurada, R. Ishikawa, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"PGTI: Pose-Graph Topological Integrity for Map Quality Assessment in SLAM,"
Robotics. 2025; 14(12):189.
[code]
S. Xie, K. Sakurada, R. Ishikawa, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"PGTI: Pose-Graph Topological Integrity for Map Quality Assessment in SLAM,"
Robotics. 2025; 14(12):189.
[code]
This study provides a spherical harmonics (SH) based fast structural representation (SH-FS)
in visual SLAM using sparse point clouds, which extracts the structure information from sparse points into single vector.
SH-FS was applied in conventional feature-based loop closing process.
Furthermore, a structure-aware loop closing method in visual SLAM was proposed to improve the robustness of SLAM systems.
To take advantage of the drone's wide field of view,
we developed a drone pose estimation system from the ground vehicle.
In this system, the relative pose is obtained by direct measurement by LiDAR and
indirect measurement of the camera's vanishing directions.
We proposed a concept to attach the SLAM-device onto a robot and quickly realize the robot navigation in 3D space.
The proposed method calibrates SLAM-device and robot itself by using the relative poses obtained by several robot movements and clarified the efficient ones for the calibration according to the DoF of the robot.
Furthermore, the relative pose is dynamically refined so that the contact between the environment and the robot maintains the geometric consistency.
-
Pesticide spraying is essential for growing crops, but food safety and cost are significant issues.
We have, therefore, developed a system to detect and remove worms using a quadruped robot capable of moving over uneven terrain.
-
 S. Balasooriya, Y. Sato, T. Oishi,
"Autonomous Robotic Platform for Proximal Data Collection Amongst Foliage Utilizing an Anisotropically Flexible Manipulator,"
The 2024 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Ha Long, Vietnam, 2024.
S. Balasooriya, Y. Sato, T. Oishi,
"Autonomous Robotic Platform for Proximal Data Collection Amongst Foliage Utilizing an Anisotropically Flexible Manipulator,"
The 2024 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Ha Long, Vietnam, 2024.
-
 H. Hansen, Y. Liu, R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, Y. Sato,
"Quadruped Robot Platform for Selective Pesticide Spraying,"
18th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Hamamatsu, Japan, 2023. pp. 1-6.
H. Hansen, Y. Liu, R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, Y. Sato,
"Quadruped Robot Platform for Selective Pesticide Spraying,"
18th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Hamamatsu, Japan, 2023. pp. 1-6.
-
We proposed an event camera tracking method for object manipulation by robots.
The method employs a unified camera projection model for various lenses, and an error function and optimization method that takes motion blur into account.
-
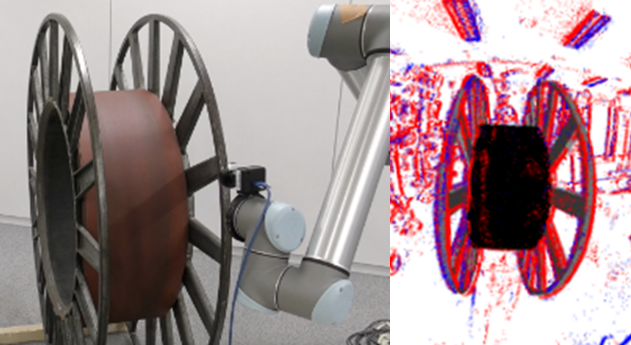 Y. Kang, G. Caron, R. Ishikawa, A. Escande, K. Chappellet, R. Sagawa, T. Oishi,
"Direct 3D model-based object tracking with event camera by motion interpolation,"
2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 2024, pp. 2645-2651.
Y. Kang, G. Caron, R. Ishikawa, A. Escande, K. Chappellet, R. Sagawa, T. Oishi,
"Direct 3D model-based object tracking with event camera by motion interpolation,"
2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 2024, pp. 2645-2651.
This study proposes a learning-based method to detect four different types of edges in 2D images.
The network architecture is based on the SWIN Transformer and is capable of extracting fine edges by using Dice loss.
-
We propose a non-learning depth completion method for a sparse depth map captured using a LiDAR sensor guided by a pair of stereo images.
The proposed selective stereo matching (SSM) method searches the most appropriate depth value for each image pixel from its neighborly projected LiDAR points based on an energy minimization framework.
This depth selection approach can handle any type of mis-projection.
Moreover, SSM has an advantage in terms of long-range depth accuracy because it directly uses the LiDAR measurement rather than the depth acquired from the stereo.
-
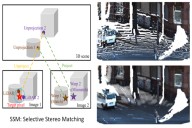 Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, K. Kurata, N. Ito, J. Shimamura, T. Oishi,
"Non-Learning Stereo-Aided Depth Completion Under Mis-Projection via Selective Stereo Matching,"
in
IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 136674-136686, 2021.
Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, K. Kurata, N. Ito, J. Shimamura, T. Oishi,
"Non-Learning Stereo-Aided Depth Completion Under Mis-Projection via Selective Stereo Matching,"
in
IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 136674-136686, 2021.
We proposed methods for estimating a dense depth map from a sparse LIDAR point cloud and images.
Our unsupervised approach is a real-time dense depth completion from sparse depth maps guided by a single image.
Our method generates smooth depth maps while preserving discontinuity between different objects.
The key idea is a Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor (B-ADT)
which can eliminate smoothness constraint at intended positions and directions
by applying variational regularization.
-
 Y. Yao, M. Roxas, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, J. Shimamura, and T. Oishi,
"Discontinuous and Smooth Depth Completion with Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 5128-5135, Oct. 2020.
arXiv:2006.14374
Y. Yao, M. Roxas, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, J. Shimamura, and T. Oishi,
"Discontinuous and Smooth Depth Completion with Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 5128-5135, Oct. 2020.
arXiv:2006.14374
Another approach relies on a directionally biased propagation of known depth to missing areas based on semantic segmentation.
Additionally, we classify different object boundaries as either occluded or connected
to limit the extent of the data propagation.
At the regions with inevitably missing point cloud data,
we depend on estimated depth using motion stereo.
We propose a real-time dense 3D mapping method for fisheye cameras without explicit rectification and undistortion.
We extend the conventional variational stereo method by constraining the correspondence search
along the epipolar curve using a trajectory field induced by camera motion.
We also propose a fast way of generating the trajectory field without increasing the processing time
compared to conventional rectified methods.
Teleoperation
-
We proposed a method to generate robot motions for vision-based teleoperation systems.
Task Model performs recognition and transmission of human motions
and can simultaneously solve the issues of the structural differences
between the human and the humanoid robot and time delays.
We also developed a method of articulation modeling using an RGB-D sensor.
The articulation parameters are estimated by a fusion of hand motion and point-cloud alignment.
-
 L. Fu, R. Ishikawa, Y. Sato and T. Oishi,
"CAPT: Category-level Articulation Estimation from a Single Point Cloud Using Transformer,"
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2024), 2024.
L. Fu, R. Ishikawa, Y. Sato and T. Oishi,
"CAPT: Category-level Articulation Estimation from a Single Point Cloud Using Transformer,"
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2024), 2024.
-
 R. Hartant, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Hand-Motion-guided Articulation and Segmentation Estimation,"
The 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples Italy, 2020,
arXiv:2005.03691.
[src]
[video]
R. Hartant, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Hand-Motion-guided Articulation and Segmentation Estimation,"
The 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples Italy, 2020,
arXiv:2005.03691.
[src]
[video]
-
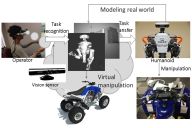 M. Ogawa, K. Honda, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Development of interface for teleoperation of humanoid robot using task model method,"
Proc. 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Dec. 2016, Sapporo, Japan.
M. Ogawa, K. Honda, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Development of interface for teleoperation of humanoid robot using task model method,"
Proc. 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Dec. 2016, Sapporo, Japan.
M. Ogawa, K. Honda, Y. Sato, S. Kudoh, T. Oishi, K. Ikeuchi,
"Motion Generation of the Humanoid Robot for Teleoperation by Task Model,"
Proc. 24th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN),
pp. 71-76, Sept. 1, 2015, Kobe Japan.
 S. Xie, K. Sakurada, R. Ishikawa, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"PGTI: Pose-Graph Topological Integrity for Map Quality Assessment in SLAM,"
Robotics. 2025; 14(12):189.
[code]
S. Xie, K. Sakurada, R. Ishikawa, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"PGTI: Pose-Graph Topological Integrity for Map Quality Assessment in SLAM,"
Robotics. 2025; 14(12):189.
[code]
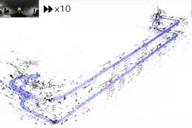 S. Xie, R. Ishikawa, K. Sakurada, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"Fast Structural Representation and Structure-aware Loop Closing for Visual SLAM,"
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots (IROS), pp. 6396-6403, 2022.
[video]
[code]
S. Xie, R. Ishikawa, K. Sakurada, M. Onishi and T. Oishi,
"Fast Structural Representation and Structure-aware Loop Closing for Visual SLAM,"
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots (IROS), pp. 6396-6403, 2022.
[video]
[code]
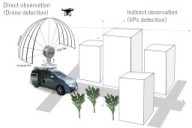 J. Hausberg, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas. T. Oishi,
"Relative Drone - Ground Vehicle Localization using LiDAR and Fisheye Cameras through Direct and Indirect Observations,"
arXiv:2011.07008,
2020.
[video]
J. Hausberg, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas. T. Oishi,
"Relative Drone - Ground Vehicle Localization using LiDAR and Fisheye Cameras through Direct and Indirect Observations,"
arXiv:2011.07008,
2020.
[video]
 R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, K. Ikeuchi,
"Dynamic Calibration between a Mobile Robot and SLAM Device for
Navigation,"
The 28th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, 2019.
[ src (HoloLensRobotNav)]
[ src (HoloLens Robot ROSPackage)]
[video(long)]
[video(short)]
R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, K. Ikeuchi,
"Dynamic Calibration between a Mobile Robot and SLAM Device for
Navigation,"
The 28th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, 2019.
[ src (HoloLensRobotNav)]
[ src (HoloLens Robot ROSPackage)]
[video(long)]
[video(short)]
 S. Balasooriya, Y. Sato, T. Oishi,
"Autonomous Robotic Platform for Proximal Data Collection Amongst Foliage Utilizing an Anisotropically Flexible Manipulator,"
The 2024 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Ha Long, Vietnam, 2024.
S. Balasooriya, Y. Sato, T. Oishi,
"Autonomous Robotic Platform for Proximal Data Collection Amongst Foliage Utilizing an Anisotropically Flexible Manipulator,"
The 2024 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Ha Long, Vietnam, 2024. H. Hansen, Y. Liu, R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, Y. Sato,
"Quadruped Robot Platform for Selective Pesticide Spraying,"
18th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Hamamatsu, Japan, 2023. pp. 1-6.
H. Hansen, Y. Liu, R. Ishikawa, T. Oishi, Y. Sato,
"Quadruped Robot Platform for Selective Pesticide Spraying,"
18th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Hamamatsu, Japan, 2023. pp. 1-6. Y. Kang, G. Caron, R. Ishikawa, A. Escande, K. Chappellet, R. Sagawa, T. Oishi,
"Direct 3D model-based object tracking with event camera by motion interpolation,"
2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 2024, pp. 2645-2651.
Y. Kang, G. Caron, R. Ishikawa, A. Escande, K. Chappellet, R. Sagawa, T. Oishi,
"Direct 3D model-based object tracking with event camera by motion interpolation,"
2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 2024, pp. 2645-2651.
 L. Miao, R. Ishikawa, and T. Oishi,
"SWIN-RIND: Edge Detection for Reflectance, Illumination, Normal and Depth Discontinuity with Swin Transformer,"
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), 2023.
[video]
[code]
L. Miao, R. Ishikawa, and T. Oishi,
"SWIN-RIND: Edge Detection for Reflectance, Illumination, Normal and Depth Discontinuity with Swin Transformer,"
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), 2023.
[video]
[code]
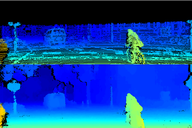 Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, and T. Oishi,
"Stereo-LiDAR Fusion by Semi-Global Matching with Discrete Disparity-Matching Cost and Semidensification,"
in
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 4548-4555, May 2025.
[code]
[bib]
Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, and T. Oishi,
"Stereo-LiDAR Fusion by Semi-Global Matching with Discrete Disparity-Matching Cost and Semidensification,"
in
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 4548-4555, May 2025.
[code]
[bib]
 Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, K. Kurata, N. Ito, J. Shimamura, T. Oishi,
"Non-Learning Stereo-Aided Depth Completion Under Mis-Projection via Selective Stereo Matching,"
in
IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 136674-136686, 2021.
Y. Yao, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, K. Kurata, N. Ito, J. Shimamura, T. Oishi,
"Non-Learning Stereo-Aided Depth Completion Under Mis-Projection via Selective Stereo Matching,"
in
IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 136674-136686, 2021.
 Y. Yao, M. Roxas, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, J. Shimamura, and T. Oishi,
"Discontinuous and Smooth Depth Completion with Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 5128-5135, Oct. 2020.
arXiv:2006.14374
Y. Yao, M. Roxas, R. Ishikawa, S. Ando, J. Shimamura, and T. Oishi,
"Discontinuous and Smooth Depth Completion with Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 5128-5135, Oct. 2020.
arXiv:2006.14374
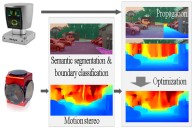 A. Hirata, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Real-Time Dense Depth Estimation using Semantically-Guided LIDAR Data Propagation and Motion Stereo,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 3806-3811, Oct. 2019.
[video]
[ src (MATLAB for accuracy comparison)]
A. Hirata, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Real-Time Dense Depth Estimation using Semantically-Guided LIDAR Data Propagation and Motion Stereo,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 3806-3811, Oct. 2019.
[video]
[ src (MATLAB for accuracy comparison)]
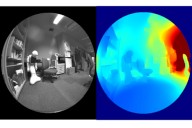 M. Roxas and T. Oishi,
"Variational Fisheye Stereo,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1303-1310, April 2020.
arXiv:1909.07545
[ src]
[video(result)]
[video(presentation)]
M. Roxas and T. Oishi,
"Variational Fisheye Stereo,"
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1303-1310, April 2020.
arXiv:1909.07545
[ src]
[video(result)]
[video(presentation)]
 L. Fu, R. Ishikawa, Y. Sato and T. Oishi,
"CAPT: Category-level Articulation Estimation from a Single Point Cloud Using Transformer,"
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2024), 2024.
L. Fu, R. Ishikawa, Y. Sato and T. Oishi,
"CAPT: Category-level Articulation Estimation from a Single Point Cloud Using Transformer,"
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2024), 2024.
 R. Hartant, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Hand-Motion-guided Articulation and Segmentation Estimation,"
The 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples Italy, 2020,
arXiv:2005.03691.
[src]
[video]
R. Hartant, R. Ishikawa, M. Roxas, T. Oishi,
"Hand-Motion-guided Articulation and Segmentation Estimation,"
The 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples Italy, 2020,
arXiv:2005.03691.
[src]
[video]
 M. Ogawa, K. Honda, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Development of interface for teleoperation of humanoid robot using task model method,"
Proc. 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Dec. 2016, Sapporo, Japan.
M. Ogawa, K. Honda, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Development of interface for teleoperation of humanoid robot using task model method,"
Proc. 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Dec. 2016, Sapporo, Japan.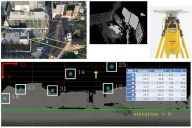 A. Kumar, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Identifying Reflected GPS Signals and Improving Position Estimation Using 3D Map Simultaneously Built with Laser Range Scanner,"
13th ITS Asia-Pacific Forum, Auckland, New Zealand, April 2014.
A. Kumar, Y. Sato, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Identifying Reflected GPS Signals and Improving Position Estimation Using 3D Map Simultaneously Built with Laser Range Scanner,"
13th ITS Asia-Pacific Forum, Auckland, New Zealand, April 2014.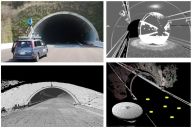 L. Xue, S. Ono, A. Banno, T. Oishi, Y. Sato, K. Ikeuchi,
"Global 3D Modeling and its Evaluation for Large-Scale Highway Tunnel using Laser Range Sensor,"
In Proc. 19th ITS World Congress Vienna, Oct. 2012, Austria. (Best Paper Award)
L. Xue, S. Ono, A. Banno, T. Oishi, Y. Sato, K. Ikeuchi,
"Global 3D Modeling and its Evaluation for Large-Scale Highway Tunnel using Laser Range Sensor,"
In Proc. 19th ITS World Congress Vienna, Oct. 2012, Austria. (Best Paper Award) Z. Wang, M. Kagesawa, S. Ono, A. Banno, T. Oishi, K. Ikeuchi,
"Detection of Emergency Telephone Indicators in a Tunnel Environment,"
International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, Jan. 2014.
Z. Wang, M. Kagesawa, S. Ono, A. Banno, T. Oishi, K. Ikeuchi,
"Detection of Emergency Telephone Indicators in a Tunnel Environment,"
International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, Jan. 2014.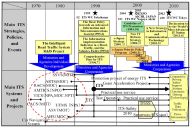 K. Koide, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Historical Analysis of the ITS Progress of Japan,"
International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, pp. 1-10, 2015.
K. Koide, T. Oishi and K. Ikeuchi,
"Historical Analysis of the ITS Progress of Japan,"
International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, pp. 1-10, 2015. 

